
– SNMPv2-Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol, a draft Internet standard, defined in RFCs 1902 through 1907.
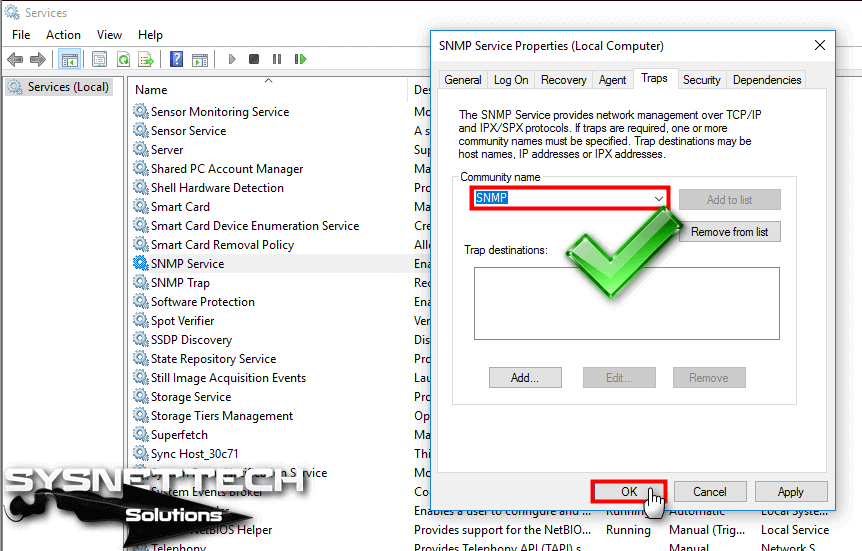
Traps can mean improper user authentication, restarts, link status (up or down), MAC address tracking, closing of a TCP connection, loss of connection to a neighbor, or other significant events. Traps are messages alerting the SNMP manager to a condition on the network. The agent can also respond to a manager’s requests to get or set data.Īn agent can send unsolicited traps to the manager. The agent gathers data from the MIB, the repository for information about device parameters and network data. A manager can get a value from an agent or store a value into the agent. The SNMP agent contains MIB variables whose values the SNMP manager can request or change. To configure SNMP on the access point, you define the relationship between the manager and the agent. The agent and management information base (MIB) reside on the access point. The SNMP manager can be part of a network management system (NMS) such as Cisco Prime Infrastructure. SNMP is an application-layer protocol that provides a message format for communication between SNMP managers and agents. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco IOS Command Reference for Cisco Aironet Access Points for this release. This chapter describes how to configure the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) on your access point.

9 Configuring an Access Point as a Local Authenticator.4 Configuring the Access Point for the First Time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
